Table of Contents

The RRB Junior Engineer (RRB JE) Computer-Based Test (CBT) 2 assesses candidates across several subjects. The Railway Recruitment Board (RRB) conducts the Junior Engineer (RRB JE) Exam in multiple stages, with CBT 2 being the most crucial for selection.
The Railway Recruitment Board (RRB) conducts the Junior Engineer (RRB JE) CBT 2 exam to recruit candidates for various technical positions, including Civil Engineering. Candidates appearing for RRB JE 2024 must be well-versed with the exam pattern and syllabus to prepare efficiently.
| You Tube | Click Here |
| Click Here | |
| Telegram | Click Here |
Here’s an overview of the exam pattern, syllabus & books.
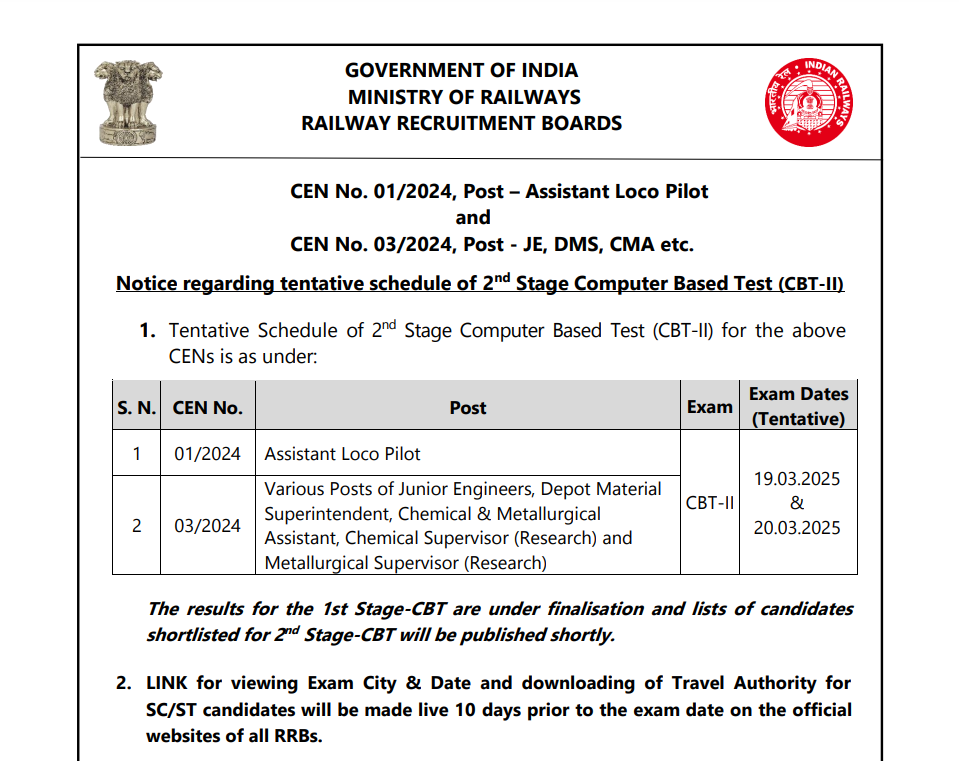
RRB JE 2024 CBT 2 Exam Date
The official exam dates for RRB JE CBT 2 (2024) have been announced. The exam will be held on the following dates:
| Exam Stage | Date |
| RRB JE CBT 2 | 19/03/2025 |
| RRB JE CBT 2 | 20/03/2025 |
Also Read: UP BSc Nursing Exam Dates
Candidates are advised to regularly check the official RRB website for updates.
RRB JE CBT 2 Exam Pattern:
| Exam Name | RRB JE CBT 2 |
| Total Questions | 150 |
| Total Marks | 150 |
| Duration | 2 hours (120 minutes) |
| Negative Marking | 1/3 mark deducted for each incorrect answer |
RRB JE 2024 CBT 2 Subject-wise Distribution:
| Subject | Number of Questions | Marks |
| General Awareness | 15 | 15 |
| Physics and Chemistry | 15 | 15 |
| Basics of Computers and Applications | 10 | 10 |
| Basics of Environment and Pollution Control | 10 | 10 |
| Technical Abilities | 100 | 100 |
| Total | 150 | 150 |
RRB JE 2024 CBT 2 Detailed Syllabus for Non – Technical:
1. General Awareness:
- Current Affairs
- Indian Geography
- Culture and History of India, including the Freedom Struggle
- Indian Polity and Constitution
- Indian Economy
- Environmental Issues concerning India and the World
- Sports
- General Scientific and Technological Developments
2. Physics and Chemistry:
Basic concepts from Class 10 and 12 level in Physics and Chemistry are covered.
- Units and Measurements
- Motion and Laws of Motion
- Work, Energy, and Power
- Heat and Thermodynamics
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Metals and Non-Metals
- Organic and Inorganic Chemistry Basics
3. Basics of Computers and Applications:
- Computer Architecture
- Input and Output Devices
- MS Office
- Storage Devices
- Operating Systems (Windows, Unix, Linux)
- Internet and Email
- Websites and Web Browsers
- Networking
- Computer Viruses
4. Basics of Environment and Pollution Control:
- Basics of Environment
- Adverse Effects of Environmental Pollution and Control Strategies
- Types of Pollution (Air, Water, Noise) and their Effects and Control
- Waste Management
- Global Warming
- Acid Rain
- Ozone Depletion
5. Technical Abilities:
The syllabus varies based on the specific engineering discipline (e.g., Mechanical, Civil, Electrical, Electronics, Computer Science).
This is the most crucial section, carrying 100 marks, covering core Civil Engineering topics.
| Topics | Sub-topics |
| Building Materials | Properties, Classification, and Uses of Materials |
| Surveying | Principles, Instruments, Measurement Techniques |
| Estimating, Costing & Valuation | Calculation of Quantities, Rate Analysis, Valuation Methods |
| Soil Mechanics | Classification, Properties of Soil, Compaction, Consolidation |
| Hydraulics & Fluid Mechanics | Fluid Properties, Flow Measurement, Pumps & Turbines |
| Irrigation Engineering | Types of Irrigation, Canals, Water Logging, Drainage Systems |
| Transportation Engineering | Railway, Highway Engineering, Traffic Control |
| Structural Analysis | Types of Beams, Trusses, Loads, Stress & Strain |
| Concrete & Steel Structures | Properties of Concrete, Reinforced Cement Concrete (RCC), Design of Steel Structures |
| Construction Management | Project Planning, PERT & CPM Techniques, Construction Equipment |
| Environmental Engineering | Water Supply, Sewage Treatment, Solid Waste Management |
RRB JE 2024 CBT 2 Detailed syllabus for Technical:
1. Engineering Mechanics- Force (resolution of force, moment of force, force system, composition of forces), Equilibrium, Friction, Centroid and Centre of gravity, Simple machines.
2. Building Construction- Building components (substructure, superstructure), type of structure (load bearing, framed and composite structures).
3. Building materials- Masonry materials (stones, bricks, and mortars), Timber and miscellaneous materials (glass, plastic, Fibre, aluminium steel, galvanized iron, bitumen, PVC, CPVC, and PPF).
4. Construction of substructure- job layout, earthwork, foundation (types, dewatering, coffer dams, bearing capacity).
5. Construction of superstructure- stone masonry, brick masonry, Hollow concrete block masonry, composite masonry, cavity wall, doors and windows, vertical communication (stairs, lifts, escalators), scaffolding and shoring.
6. Building finishes- Floors (finishes, process of laying), walls (plastering, pointing, painting) and roofs (roofing materials including RCC).
7. Building maintenance- Cracks (causes, type, repairs- grouting, guniting, epoxy etc.), settlement (causes and remedial measures), and re-baring techniques.
8. Building drawing- Conventions (type of lines, symbols), planning of building (principles of planning for residential and public buildings, rules and byelaws), drawings (plan, elevation, section, site plan, location plan, foundation plan, working drawing), perspective drawing.
9. Concrete Technology- Properties of various types/grades of cement, properties of coarse and fine aggregates, properties of concrete (water cement ratio, properties of fresh and hardened concrete), Concrete mix design, testing of concrete, quality control of concrete (batching, formwork, transportation, placing, compaction, curing, waterproofing), extreme weather concreting and chemical admixtures, properties of special concrete (ready mix, RCC, pre-stressed, Fibre reinforced, precast, high performance )
10. Surveying- Types of survey, chain and cross staff survey (principle, ranging,
triangulation, chaining, errors, finding area), compass survey (principle, bearing of line, prismatic compass, traversing, local attraction, calculation of bearings, angles and local attraction) leveling (dumpy level, recording in level book, temporary adjustment, methods of reduction of levels, classification of leveling, tilting level, auto level, sources of errors, precautions and difficulties in leveling), contouring (contour interval, characteristics, method of locating, interpolation, establishing grade contours, uses of contour maps), area and volume measurements, plane table survey (principles, setting, method), theodolite survey (components, adjustments, measurements, traversing), Tacheometric survey, curves (types, setting out), advanced survey equipment, aerial survey and remote sensing.
11. Computer Aided Design- CAD Software (AutoCAD, Auto Civil, 3D Max etc.), CAD commands, generation of plan, elevation, section, site plan, area statement, 3D view.
12. Geo Technical Engineering- Application of Geo Technical Engineering in design of foundation, pavement, earth retaining structures, earthen dams etc., physical properties of soil, permeability of soil and seepage analysis, shear strength of soil, bearing capacity of soil, compaction and stabilization of soil, site investigation and sub soil exploration.
13. Hydraulics- properties of fluid, hydrostatic pressure, measurement of liquid pressure in pipes, fundamentals of fluid flow, flow of liquid through pipes, flow through open channel, flow measuring devices, hydraulic machines.
14. Irrigation Engineering- Hydrology, investigation and reservoir planning, percolation tanks, diversion head works.
15. Mechanics of Structures- Stress and strain, shear force and bending moment, moment of inertia, stresses in beams, analysis of trusses, strain energy.
16. Theory of structures- Direct and bending stresses, slope and deflection, fixed beam, continuous beam, moment distribution method, columns.
17. Design of Concrete Structures- Working Stress method, Limit State method, analysis and design of singly reinforced and doubly reinforced sections, shear, bond and development length, analysis and design of T Beam, slab, axially loaded column and footings.
18. Design of Steel Structures- Types of sections, grades of steel, strength characteristics, IS Code, Connections, Design of tension and compression members, steel roof truss, beams, column bases.
19. Transportation Engineering- Railway Engineering (alignment and gauges, permanent way, railway track geometrics, branching of tracks, stations and yards, track maintenance), Bridge engineering (site selection, investigation, component parts of bridge, permanent and temporary bridges, inspection and maintenance), Tunnel engineering (classification, shape and sizes, tunnel investigation and surveying, method of tunneling in various strata, precautions, equipment, explosives, lining and ventilation). Highway Engineering- Road Engineering, investigation for road project, geometric design of highways, construction of road pavements and materials, traffic engineering, hill roads, drainage of roads, maintenance and repair of roads.
20. Environmental Engineering- Environmental pollution and control, public water supply, domestic sewage, solid waste management, environmental sanitation, and plumbing.
21. ADVANCED CONSTRUCTION TECHNIQUES AND EQUIPMENTS – Fibers and plastics, artificial timber, advanced concreting methods (under water concreting, ready mix concrete, tremix concreting, special concretes), formwork, prefabricated construction, soil reinforcing techniques, hoisting and conveying equipment, earth moving machinery (exaction and compaction equipment), concrete mixers, stone crushers, pile driving equipment, working of hot mix bitumen plant, bitumen paver, floor polishing machines.
22. Estimating and Costing- Types of estimates (approximate, detailed), mode of measurements and rate analysis.
23. Contracts and Accounts- Types of engineering contracts, Tender and tender documents, payment, specifications.
Important FAQs on RRB JE 2024 CBT 2 Civil Engineering Exam
When will the RRB JE 2024 CBT 2 Exam be conducted?
The exact date has not been announced yet. Candidates should regularly check the official website for updates.
Is there negative marking in RRB JE CBT 2?
Yes, 1/3 mark will be deducted for each incorrect answer.
What are the qualifying marks for RRB JE CBT 2?
The expected qualifying marks are:
UR & EWS: 40%
OBC & SC: 30%
ST: 25%
Which section has the highest weightage in RRB JE CBT 2 Civil Engineering?
The Technical Abilities section carries 100 marks, making it the most important section.
Can I use a calculator in RRB JE CBT 2?
No, the use of a calculator is not allowed during the exam.
How can I prepare for the RRB JE Civil Engineering exam?
Study the core Civil Engineering subjects thoroughly.
Refer to previous year question papers.
Attempt mock tests regularly.
Focus on time management and accuracy.
